V113. Implicit type conversion from memsize to double type or vice versa.
The analyzer found a possible error related to the implicit conversion of memsize type to 'double' type of vice versa. The possible error may consist in the impossibility of storing the whole value range of memsize type in variables of 'double' type.
Let's study an example.
SIZE_T size = SIZE_MAX;
double tmp = size;
size = tmp; // x86: size == SIZE_MAX
// x64: size != SIZE_MAX'double' type has size 64 bits and is compatible IEEE-754 standard on 32-bit and 64-bit systems. Some programmers use 'double' type to store and work with integer types.
The given example may be justified on a 32-bit system for 'double' type has 52 significant bits and is capable to store a 32-bit integer value without a loss. But while trying to store an integer number in a variable of 'double' type the exact value can be lost (see picture).
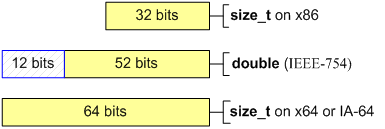
If an approximate value can be used for the work algorithm in your program no corrections are needed. But we would like to warn you about the results of the change of behavior of a code like this on 64-bit systems. In any case it is not recommended to mix integer arithmetic with floating point arithmetic.
Additional materials on this topic:
- 64-bit Lessons. Lesson 18. Pattern 10. Storage of integer values in double.

